HQ Team
November 20, 2022: Swedish researchers have found a potential biomarker for severe Covid-19 disease that has claimed the lives of more than 6.5 million people globally.
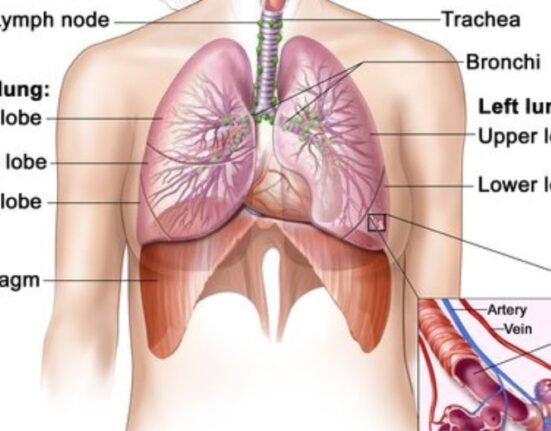
Patients with acute Covid-19 infection have increased levels of the cytokine IL-26 in their blood, researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden said. They have spotted several metabolic processes SARS-Cov-2 uses to attack lung tissue.
Cytokine is a protein that affects the immune system. Some cytokines stimulate the immune system, and others slow it down. They can also be made in the laboratory and used to help the body fight cancer, infections, and other diseases.
High IL-26 levels correlate with an exaggerated inflammatory response that signifies severe disease cases. The findings indicate that IL-26 is a potential biomarker for severe COVID-19.
The emergence of new viral variants, limited distribution of the vaccine and declining immunity are problems driving scientists to find more efficacious treatments for the disease.
Improved diagnostics
“We need to understand more about underlying immunological mechanisms to find better treatments. There is also a need for improved diagnostics in COVID 19-patients,” said Eduardo Cardenas, principal author of the pilot study.
For the first time, the researchers have tried to ascertain whether immune signalling through the cytokine interleukin-26 (IL-26) is involved in severe COVID-19.
“We already know that IL-26 is engaged in mobilising immune cells that combat bacterial infections in the lungs and also in chronic respiratory disease in humans,” said Anders Lindén, consultant and professor at the Institute of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institutet.
“What’s more, IL-26 has antiviral and antibacterial effects.”
To find out how the molecule is involved in COVID-19, the scientists recruited 49 patients who were hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2-infection. Forty-four had severe symptoms and needed oxygen therapy.
Control group
The patients were recruited at a hospital in Stockholm from June 2020 to January 2021. The researchers also recruited a control group of 27 healthy individuals during the same period.
The researchers then measured levels of IL-26 protein and other inflammatory compounds in the blood.
“We can show for the first time that blood levels of the cytokine IL-26 are much higher in patients with COVID-19 than in healthy controls,” says Dr Cardenas.
The researchers could also see that the increase was associated with the so-called cytokine storm – an excessive and dangerous inflammatory response that signifies severe cases of COVID-19.
“Our discovery gives us a potential biomarker for severe COVID-19, but given the antiviral effects of IL-26, we may also have identified a new therapeutic target,” said professor Linden.
A biomarker is a biological molecule found in blood, other body fluids, or tissues that is a sign of a standard or abnormal process, condition, or disease. It can be employed to see how well the body responds to a treatment for an illness or condition.
The results are promising but “are preliminary and warrant further study with a larger patient cohort,” said doctor Cardenas,