HQ Team
November 25, 2023: The first Mpox patient to contact the disease through sexual contact has been confirmed by the WHO in Congo as the global health agency reported its spread to Western Pacific and European regions, South-East Asia, and the Region of the Americas.
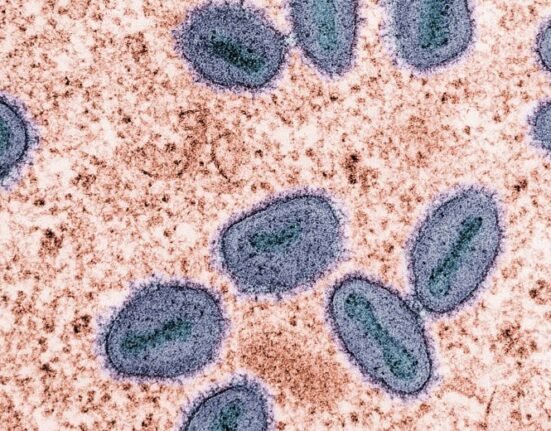
The latest Situation Report issued by the World Health Organization (WHO), addresses the evolving epidemiology of Mpox, including confirming it as a sexually transmitted disease (STD)caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV).
Global case overview
A total of 668 new laboratory-confirmed cases of Mpox were documented worldwide in October 2023, originating from 29 countries. The largest outbreak has been recorded in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Notably, the Western Pacific and European regions bore the highest case burdens, with the South-East Asia Region and the Region of the Americas closely following. The African Region reports eight cases; Eastern Mediterranean Region reports one.
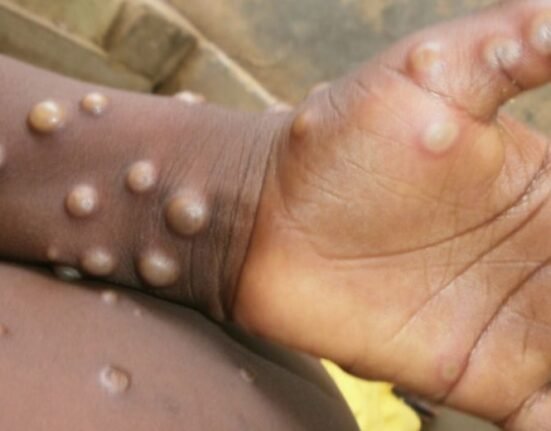
Sexual encounters have been reported as the most common mode of transmission (82.9%). The reported symptoms are consistent and include rash, fever, and systemic/genital rash.
The Congo region
The Mpox virus was first discovered in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Mpox can cause enlarged lymph nodes and a fever and can lead to severe, life-threatening complications. It gained global attention in May 2022 with an increasing number of cases that developed into an international outbreak.
The WHO confirmed 12, 569 suspected cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo since January 2023, resulting in 581 deaths with a case fatality ratio of 4.6%.
The risk assessment for the general population is rated as moderate. For specific groups such as gay men, bisexual men, and sex workers it is also put as moderate.
According to the WHO, since 2022, an epidemic of clade IIb MPXV has been ongoing globally, affecting many countries outside the African continent that had never reported Mpox previously.
Regional Breakdown
- Region of the Americas: 60,092 cases, 134 deaths; +85% change in the last month.
- European Region: 26,395 cases, 7,164 deaths; -28% change.
- Western Pacific Region: 2,586 cases, 1,201 deaths; -49% change.
- African Region: 1,981 cases, 22 deaths; -50% change.
- South-East Asia Region: 639 cases, 2 deaths; -2% change.
- Eastern Mediterranean Region: 95 cases, 1 death; +200% change.
The Disease Outbreak report provides detailed insights into the evolving situation, emphasizing the need for global attention and collaborative efforts to curb the spread of Mpox.
In a related report, the German biotechnology company, BioNTech SE announced a $ 90 million program in partnership with the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) to develop a vaccine for Mpox.
The Mpox vaccine program, labelled as BNT166, is part of BioNTech’s efforts to develop a prophylactic vaccine for a range of infectious diseases with a high medical need, according to a BioNTech statement.
The WHO report on the disease spread can be accessed here.